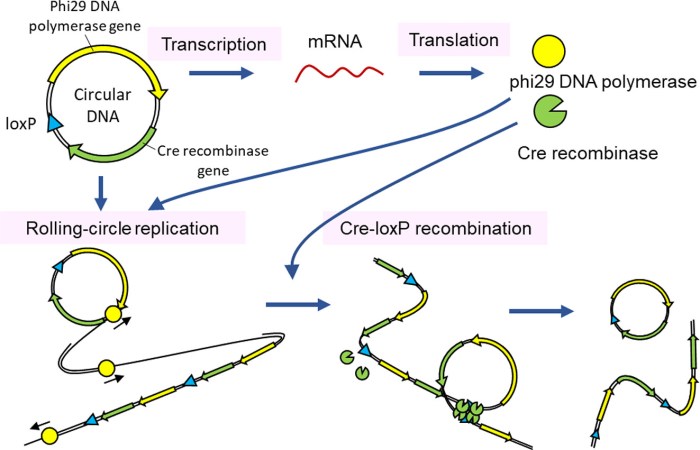
In contrast to linear dna replication circular dna replication typically – In contrast to linear DNA replication, circular DNA replication typically employs a unique mechanism that allows for continuous replication, making it essential for certain organisms and applications.
Circular DNA replication involves the formation of a circular DNA molecule, which undergoes continuous replication without the need for telomeres. This process plays a crucial role in maintaining genetic stability and is employed by various organisms, including bacteria and viruses.
1. Linear DNA Replication vs. Circular DNA Replication
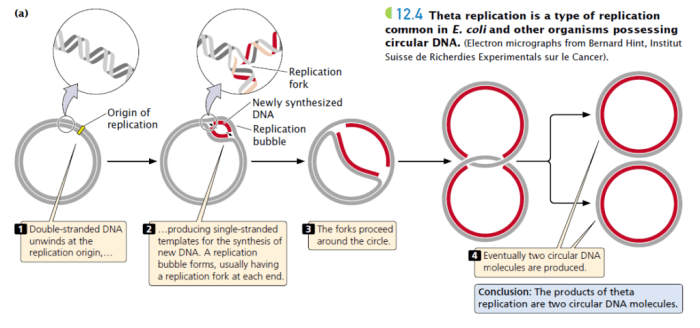
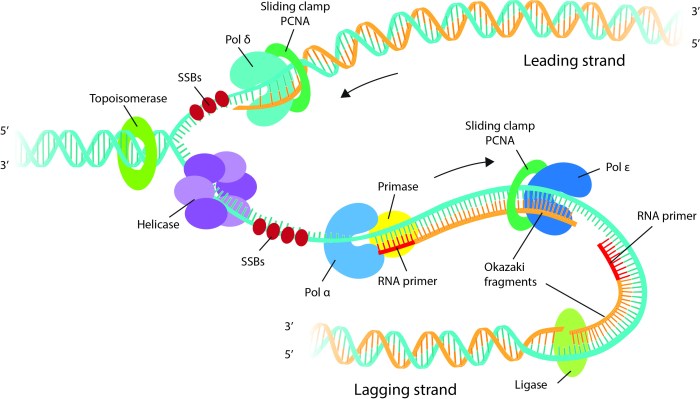
DNA replication is the process by which DNA molecules make copies of themselves. There are two main types of DNA replication: linear DNA replication and circular DNA replication.
Linear DNA replication occurs in eukaryotes, which are organisms with cells that have a nucleus. In linear DNA replication, the DNA molecule is a single, linear strand. The replication process begins at the ends of the DNA molecule and proceeds towards the center.
As the DNA molecule is replicated, two new DNA molecules are created, each of which is identical to the original DNA molecule.
Circular DNA replication occurs in prokaryotes, which are organisms that do not have a nucleus. In circular DNA replication, the DNA molecule is a single, circular strand. The replication process begins at a specific point on the DNA molecule and proceeds around the circle.
As the DNA molecule is replicated, one new DNA molecule is created, which is identical to the original DNA molecule.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Circular DNA Replication
There are several advantages of circular DNA replication over linear DNA replication.
- Circular DNA replication is more efficient than linear DNA replication because it does not require the synthesis of new DNA at the ends of the DNA molecule.
- Circular DNA replication is more stable than linear DNA replication because it does not have any free ends that can be damaged.
- Circular DNA replication is more easily repaired than linear DNA replication because it does not require the synthesis of new DNA at the ends of the DNA molecule.
There are also some disadvantages of circular DNA replication.
- Circular DNA replication is not as flexible as linear DNA replication because it cannot be broken down into smaller pieces.
- Circular DNA replication can be more difficult to manipulate than linear DNA replication because it cannot be cut with restriction enzymes.
Mechanisms of Circular DNA Replication
The mechanisms of circular DNA replication are not fully understood. However, it is known that the replication process is initiated by a protein called the initiator protein. The initiator protein binds to a specific site on the DNA molecule and begins to unwind the DNA double helix.
Once the DNA double helix is unwound, the DNA polymerase enzyme can begin to synthesize new DNA strands. The DNA polymerase enzyme adds nucleotides to the new DNA strands in a complementary fashion, meaning that the sequence of nucleotides in the new DNA strands is complementary to the sequence of nucleotides in the original DNA strands.
The replication process continues until the entire DNA molecule has been replicated. Once the replication process is complete, the two new DNA molecules are separated and each new DNA molecule is packaged into a new nucleosome.
Applications of Circular DNA Replication, In contrast to linear dna replication circular dna replication typically
Circular DNA replication is used in a variety of applications, including gene therapy, vaccine development, and the production of recombinant proteins.
In gene therapy, circular DNA molecules are used to deliver genes to cells that are missing or have defective genes. The circular DNA molecules are taken up by the cells and the genes are expressed, which can correct the genetic defect.
In vaccine development, circular DNA molecules are used to produce vaccines that are more stable and effective than traditional vaccines. The circular DNA molecules are taken up by the cells and the antigens are expressed, which can stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies against the antigen.
In the production of recombinant proteins, circular DNA molecules are used to produce proteins that are not naturally produced by the organism. The circular DNA molecules are taken up by the cells and the proteins are expressed, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as research, diagnostics, and therapeutics.
Helpful Answers: In Contrast To Linear Dna Replication Circular Dna Replication Typically
What are the key differences between circular and linear DNA replication?
Circular DNA replication involves continuous replication without telomeres, while linear DNA replication requires telomeres to prevent chromosome shortening.
Why is circular DNA replication important for certain organisms?
Circular DNA replication is essential for organisms that require continuous replication, such as bacteria and viruses, which lack telomerase.
What are the applications of circular DNA replication in biotechnology?
Circular DNA is used in gene therapy, vaccine development, and other applications due to its ability to maintain genetic stability and facilitate efficient gene expression.