Jeremy has parkinson’s disease a progressive neurodegenerative – Jeremy’s Parkinson’s Journey: A Progressive Neurodegenerative Battle delves into the complexities of this relentless condition, unveiling the challenges, coping mechanisms, and unwavering spirit of an individual facing its progressive grip. This narrative invites us to witness Jeremy’s resilience and the profound impact of Parkinson’s on his life, relationships, and unwavering determination to live life to the fullest.
Parkinson’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, affects millions worldwide, gradually impairing motor functions and challenging cognitive abilities. Jeremy’s diagnosis marked the beginning of a transformative journey, a path paved with obstacles and triumphs, where resilience and support became his guiding lights.
Understanding Parkinson’s Disease: Jeremy Has Parkinson’s Disease A Progressive Neurodegenerative
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects the central nervous system. It primarily affects the motor system, leading to tremors, rigidity, and impaired balance and coordination.
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Certain genes have been linked to an increased risk of developing Parkinson’s, but most cases are sporadic, meaning they occur without a clear genetic cause.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s disease vary from person to person and can progress over time. Common symptoms include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowed movement), postural instability, and speech and swallowing difficulties.
Jeremy’s Journey with Parkinson’s
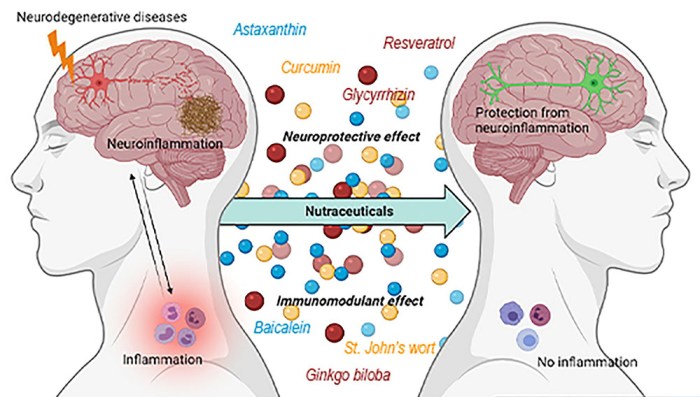
Jeremy was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease at the age of 45. Initially, he experienced mild tremors in his right hand, which he attributed to stress.
As the disease progressed, Jeremy faced challenges such as difficulty with fine motor skills, impaired balance, and fatigue. He had to adjust his lifestyle and work habits to accommodate his symptoms.
Parkinson’s disease has had a significant impact on Jeremy’s daily life and relationships. He has had to rely on support from his family and friends, and he has become an advocate for Parkinson’s awareness and research.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Systems

Jeremy has adapted to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease through a combination of physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Physical therapy helps Jeremy improve his mobility and balance. He also engages in regular exercise, such as walking and swimming, to maintain his strength and coordination.
Jeremy relies on medication to manage his tremors and other symptoms. He takes a combination of levodopa and carbidopa, which help to increase dopamine levels in the brain.
Support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals has been invaluable for Jeremy. His wife provides him with emotional support and practical assistance, while his healthcare team monitors his condition and adjusts his treatment as needed.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
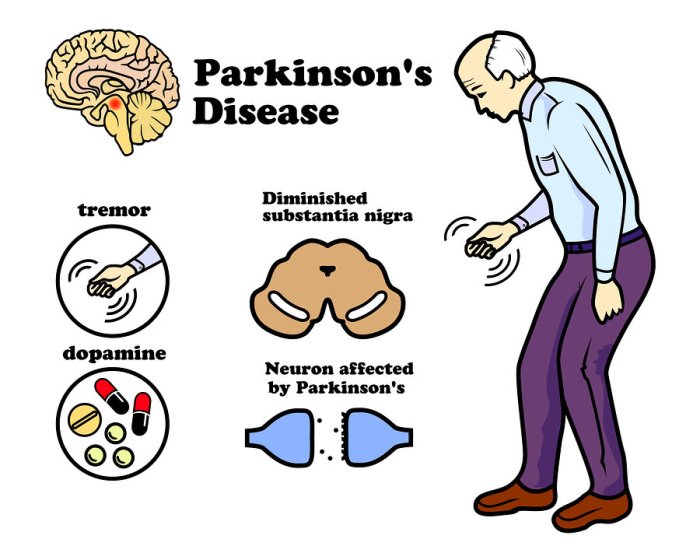
There is currently no cure for Parkinson’s disease, but medical treatments can help to manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Medications are the primary treatment for Parkinson’s disease. Levodopa, a dopamine precursor, is the most commonly used medication. Other medications include dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and anticholinergics.
Surgical interventions, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS), may be considered for people who do not respond well to medication. DBS involves implanting electrodes into the brain to regulate abnormal brain activity.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Complementary and alternative therapies can be used alongside medical treatments to manage the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exercise has been shown to improve mobility, balance, and overall well-being in people with Parkinson’s. Tai chi, yoga, and dance are particularly beneficial.
Dietary changes, such as reducing caffeine and alcohol intake, may help to improve symptoms. Some studies suggest that a Mediterranean diet may be beneficial.
Mindfulness-based therapies, such as meditation and mindfulness training, can help to reduce stress and improve emotional well-being in people with Parkinson’s.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Parkinson’s disease can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals.
Depression and anxiety are common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Cognitive impairment, such as memory loss and difficulty with attention, can also occur.
Coping with the emotional and psychological challenges of Parkinson’s disease requires a multidisciplinary approach. Therapy, support groups, and medication can help to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Advocacy and Awareness
Advocacy and awareness are essential for advancing research and improving the lives of people with Parkinson’s disease.
Organizations such as the Parkinson’s Disease Foundation and the Michael J. Fox Foundation fund research and provide support to individuals and families affected by Parkinson’s.
Successful advocacy campaigns have led to increased funding for research, improved access to care, and greater awareness of Parkinson’s disease.
Top FAQs
What are the common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease?
Parkinson’s disease manifests in a range of symptoms, including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowed movement), postural instability, and impaired balance.
How does Parkinson’s disease affect an individual’s daily life?
Parkinson’s disease can significantly impact daily activities, affecting mobility, coordination, speech, and cognitive function. It can also lead to social isolation and reduced quality of life.
What are the available treatments for Parkinson’s disease?
Treatment options for Parkinson’s disease include medications to manage symptoms, surgical interventions such as deep brain stimulation, and complementary therapies like exercise and speech therapy.