Practice phylogenetic trees 2 answer key pdf – Embark on a journey into the realm of phylogenetic trees with “Practice Phylogenetic Trees 2: Answer Key PDF.” This comprehensive guide empowers you to construct and interpret these intricate diagrams, unlocking the secrets of evolutionary relationships. Immerse yourself in a world of scientific discovery, where the mysteries of life’s origins unfold.
Delve into the fascinating world of phylogenetic trees, where the evolutionary relationships between species are meticulously mapped out. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the subject, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of these intricate diagrams.
Through practice exercises and an accompanying answer key, you will gain a deep understanding of phylogenetic tree construction and interpretation, empowering you to explore the depths of evolutionary history.
Phylogenetic Trees Overview: Practice Phylogenetic Trees 2 Answer Key Pdf
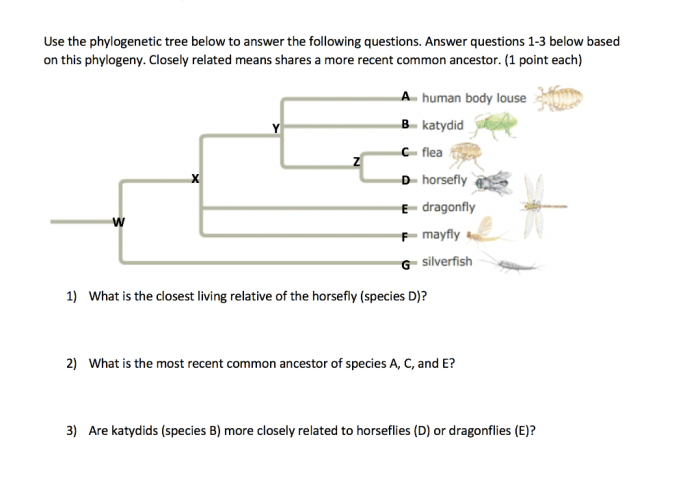
Phylogenetic trees, also known as evolutionary trees, are diagrams that represent the evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa. They are used to visualize and understand the history of life on Earth and the branching patterns of different lineages over time.
The concept of evolutionary relationships is based on the idea that all living organisms share a common ancestor and have diverged from that ancestor over time through the process of evolution. Phylogenetic trees depict these relationships by connecting different species or taxa with branches, where the length of the branches represents the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that branch.
Types of Phylogenetic Trees, Practice phylogenetic trees 2 answer key pdf
- Cladograms:Cladograms are the simplest type of phylogenetic tree and only show the branching patterns of different lineages, without indicating the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along each branch.
- Phylograms:Phylograms are similar to cladograms but include branch lengths that represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along each branch.
- Rooted Trees:Rooted trees have a designated root that represents the common ancestor of all the taxa included in the tree. This type of tree allows for the determination of the direction of evolutionary change.
- Unrooted Trees:Unrooted trees do not have a designated root and do not indicate the direction of evolutionary change. They simply show the branching patterns of different lineages.
Building Phylogenetic Trees

Phylogenetic trees are constructed using various methods, including:
- Morphological Data:Morphological data refers to the physical characteristics of organisms, such as their size, shape, and other observable traits. These characteristics can be used to infer evolutionary relationships by comparing the similarities and differences between different species.
- Molecular Data:Molecular data refers to the genetic material of organisms, such as DNA and RNA sequences. This data can be used to infer evolutionary relationships by comparing the similarities and differences in the genetic sequences of different species.
- Fossil Record:The fossil record provides evidence of past life forms and can be used to infer evolutionary relationships by examining the changes in morphology and other characteristics over time.
The selection of appropriate data for building phylogenetic trees is crucial, as it can affect the accuracy and reliability of the resulting tree. Software and algorithms are also used to assist in the construction of phylogenetic trees by analyzing the data and generating tree topologies.
Interpreting Phylogenetic Trees
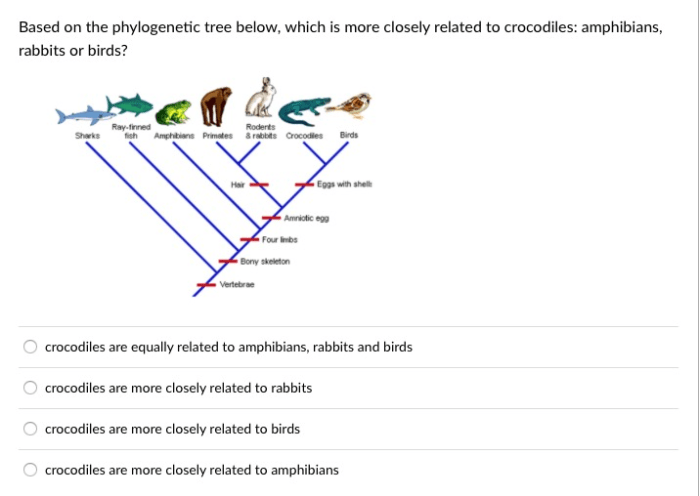
Phylogenetic trees can be interpreted to gain insights into the evolutionary history of different species or taxa. Here are some guidelines for interpreting phylogenetic trees:
- Branch Lengths:The length of a branch in a phylogenetic tree represents the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that branch. Longer branches indicate more evolutionary change, while shorter branches indicate less evolutionary change.
- Nodes:Nodes in a phylogenetic tree represent the points where different branches diverge or connect. Internal nodes represent common ancestors, while terminal nodes represent the tips of the tree and represent the individual species or taxa included in the tree.
- Tree Topology:The topology of a phylogenetic tree refers to the overall branching pattern of the tree. It can provide insights into the order in which different lineages diverged from each other and the relationships between different groups.
Applications of Phylogenetic Trees
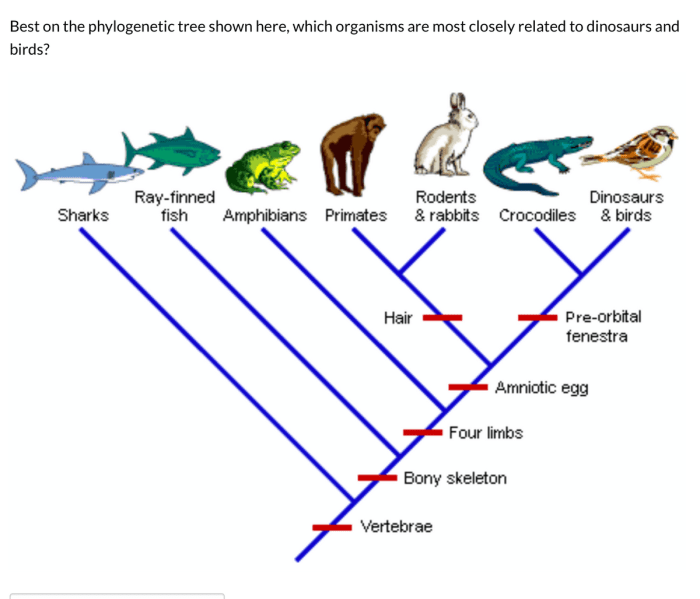
Phylogenetic trees have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Evolutionary Biology:Phylogenetic trees are used to study the evolutionary history of different species and to understand the patterns of diversification and speciation over time.
- Taxonomy:Phylogenetic trees are used to classify and organize different species into taxonomic groups based on their evolutionary relationships.
- Medicine:Phylogenetic trees are used to study the evolution of diseases and to develop new treatments and vaccines.
Phylogenetic trees have contributed significantly to our understanding of the diversity of life on Earth and the evolutionary processes that have shaped it.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of a phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees are used to represent the evolutionary relationships between different species or groups of organisms, providing a visual representation of their shared ancestry and genetic relatedness.
How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
Phylogenetic trees are typically constructed using comparative data, such as DNA sequences or morphological characteristics. By analyzing these data, scientists can infer the branching patterns and relationships between different species.
What is the importance of branch lengths in phylogenetic trees?
Branch lengths in phylogenetic trees represent the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along a particular branch. Longer branches indicate more evolutionary change, while shorter branches indicate less change.
