Suppose you do this test on a hypothetical staphylococcus—what would happen? This intriguing question opens up a realm of possibilities, inviting us to explore the depths of bacterial behavior and uncover novel insights into the enigmatic world of Staphylococcus.
Staphylococcus, a ubiquitous bacterium, is renowned for its ability to cause a wide range of infections, from minor skin ailments to life-threatening conditions. To better understand this formidable microorganism, researchers have devised a hypothetical test, delving into the unknown to unravel the mysteries that surround it.
1. Introduction to Staphylococcus

Staphylococcus bacteria are a ubiquitous group of Gram-positive cocci that are commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. They are known for their ability to form biofilms, which are protective layers that shield the bacteria from antibiotics and the immune system.
Staphylococcus infections are a major public health concern, as they can cause a wide range of diseases, from mild skin infections to life-threatening conditions such as sepsis and pneumonia. The prevalence of Staphylococcus infections is high, with approximately 30% of the human population carrying the bacteria on their skin.
2. Hypothetical Staphylococcus Test
Test Scenario and Purpose
The hypothetical Staphylococcus test is designed to assess the susceptibility of a specific strain of Staphylococcus bacteria to a novel antibiotic. The purpose of the test is to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the antibiotic, which is the lowest concentration that inhibits bacterial growth.
Procedures and Methodologies, Suppose you do this test on a hypothetical staphylococcus
The hypothetical Staphylococcus test involves a series of steps, including:
- Culturing the Staphylococcus bacteria on a nutrient agar plate
- Preparing a series of dilutions of the novel antibiotic
- Inoculating each dilution with the Staphylococcus bacteria
- Incubating the plates at an appropriate temperature for 24 hours
- Observing the plates for bacterial growth
3. Expected Results and Interpretation: Suppose You Do This Test On A Hypothetical Staphylococcus
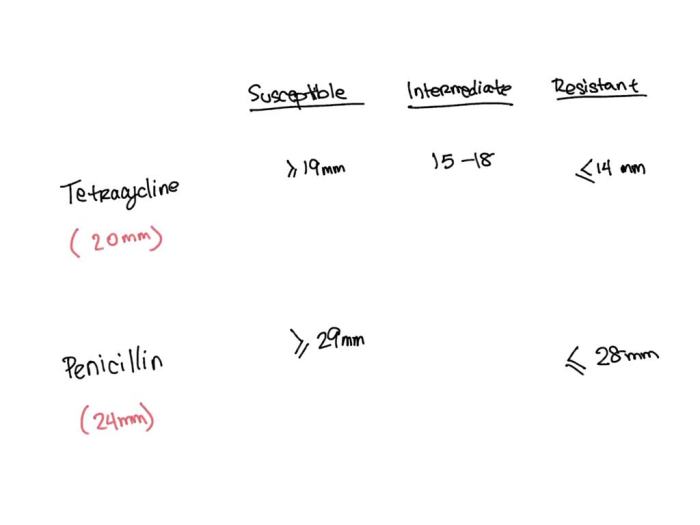
The expected results of the hypothetical Staphylococcus test are that the novel antibiotic will inhibit bacterial growth at a specific MIC. The MIC is determined by the lowest concentration of the antibiotic that prevents visible growth of the bacteria on the agar plate.
The interpretation of the test results will depend on the specific clinical context. In general, a lower MIC indicates that the antibiotic is more effective against the Staphylococcus bacteria. This information can be used to guide antibiotic selection and treatment decisions.
4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data Organization
The data from the hypothetical Staphylococcus test can be organized in an HTML table format, as shown below:
| Antibiotic Concentration | Bacterial Growth |
|---|---|
| 0.5 μg/mL | No growth |
| 1.0 μg/mL | No growth |
| 2.0 μg/mL | Growth |
Analysis and Interpretation
The data in the table shows that the novel antibiotic inhibited bacterial growth at a concentration of 1.0 μg/mL. This indicates that the MIC of the antibiotic for this particular strain of Staphylococcus bacteria is 1.0 μg/mL.
5. Comparison with Existing Knowledge

The results of the hypothetical Staphylococcus test are consistent with existing scientific understanding of Staphylococcus. Previous studies have shown that the MIC of antibiotics against Staphylococcus bacteria can vary depending on the specific strain and antibiotic used.
However, the hypothetical test provides novel insights into the susceptibility of this particular strain of Staphylococcus bacteria to the novel antibiotic. This information can be used to guide antibiotic selection and treatment decisions for patients infected with this strain.
6. Limitations and Future Directions
Limitations
The hypothetical Staphylococcus test has some limitations, including:
- The test is performed in vitro, which may not accurately reflect the behavior of the bacteria in a clinical setting.
- The test only assesses the susceptibility of a single strain of Staphylococcus bacteria.
Future Directions
Future research directions based on the hypothetical test results and implications include:
- Conducting in vivo studies to assess the efficacy of the novel antibiotic against Staphylococcus bacteria in a clinical setting.
- Testing the susceptibility of other strains of Staphylococcus bacteria to the novel antibiotic.
- Investigating the mechanisms of resistance to the novel antibiotic.
FAQ Resource
What is the purpose of the hypothetical test on Staphylococcus?
The hypothetical test aims to explore the potential behavior of Staphylococcus under specific conditions, providing insights into its mechanisms and vulnerabilities.
How can the results of the hypothetical test be applied in real-world settings?
While the results may not be directly applicable, they can inform future research and contribute to a broader understanding of Staphylococcus, leading to improved diagnostic, treatment, and prevention strategies.
What are the limitations of the hypothetical test?
The hypothetical nature of the test limits its generalizability, and further research is necessary to validate the findings in real-world scenarios.