it travels through air at roughly nyt embarks on a scientific odyssey, unraveling the captivating world of sound, light, and electromagnetic waves as they traverse the vast expanse of air. Delving into the intricacies of wave propagation, we uncover the fundamental principles governing their movement, revealing the remarkable applications that shape our daily lives.
From the harmonious melodies of sound waves to the illuminating power of light waves, the ethereal realm of radio waves to the practical utility of microwaves, this narrative unveils the multifaceted nature of these waves, exploring their distinct characteristics, behaviors, and technological significance.
Sound Waves: It Travels Through Air At Roughly Nyt

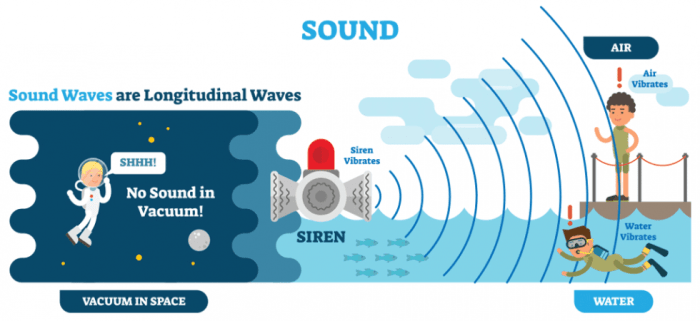
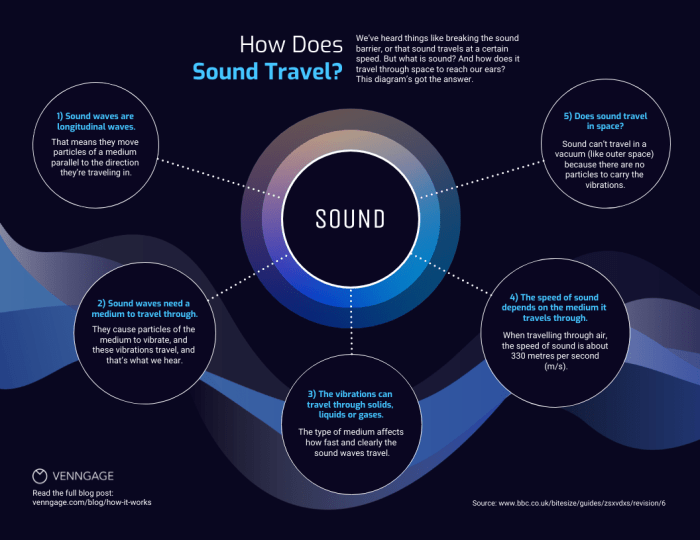
Sound waves are mechanical waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. They are caused by the vibration of particles in the medium. When an object vibrates, it causes the particles around it to vibrate, which in turn causes the next layer of particles to vibrate, and so on.
This creates a wave of energy that travels through the medium.
Factors Affecting the Speed of Sound in Air
- Temperature:The speed of sound increases with temperature. This is because the particles in the air move faster at higher temperatures, which allows the wave to travel faster.
- Pressure:The speed of sound increases with pressure. This is because the particles in the air are closer together at higher pressures, which allows the wave to travel faster.
- Humidity:The speed of sound decreases with humidity. This is because water vapor molecules are larger than air molecules, which slows down the wave.
Examples of How Sound Waves Are Used in Everyday Life, It travels through air at roughly nyt
- Speech:Sound waves are used to produce speech. When we speak, our vocal cords vibrate, which creates sound waves that travel through the air to the listener’s ears.
- Music:Sound waves are used to produce music. When a musical instrument is played, it creates sound waves that travel through the air to the listener’s ears.
- Ultrasound:Sound waves are used in ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body.
Light Waves
Light waves are electromagnetic waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. They are caused by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields. When an object emits light, it creates a wave of energy that travels through the medium.
Types of Light Waves
- Visible light:Visible light is the type of light that we can see. It has a wavelength of between 400 and 700 nanometers.
- Ultraviolet light:Ultraviolet light has a wavelength of between 10 and 400 nanometers. It is invisible to the human eye, but it can cause sunburn and skin cancer.
- Infrared light:Infrared light has a wavelength of between 700 nanometers and 1 millimeter. It is invisible to the human eye, but it can be felt as heat.
Examples of How Light Waves Are Used in Everyday Life
- Vision:Light waves are used to see. When light waves enter our eyes, they are converted into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. The brain then interprets these signals to create an image of the world around us.
- Photography:Light waves are used to take photographs. When light waves enter a camera, they are focused onto a film or sensor. The film or sensor then records the light waves, which creates an image.
- Lasers:Lasers are devices that emit a concentrated beam of light waves. Lasers are used in a variety of applications, such as laser surgery, laser cutting, and laser pointers.
Radio Waves
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or solids. They are caused by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields. When an object emits radio waves, it creates a wave of energy that travels through the medium.
Types of Radio Waves
- AM radio waves:AM radio waves have a wavelength of between 200 and 600 meters. They are used to transmit audio signals over long distances.
- FM radio waves:FM radio waves have a wavelength of between 3 and 10 meters. They are used to transmit audio signals over shorter distances.
- Microwaves:Microwaves are a type of radio wave with a wavelength of between 1 millimeter and 1 meter. They are used in a variety of applications, such as microwave ovens, radar, and satellite communications.
Examples of How Radio Waves Are Used in Everyday Life
- Radio broadcasting:Radio waves are used to transmit radio broadcasts. When a radio station broadcasts a signal, it is transmitted through the air as radio waves. The radio waves are then picked up by radio receivers, which convert them into audio signals that can be heard by the listener.
- Television broadcasting:Television signals are transmitted through the air as radio waves. The radio waves are then picked up by television receivers, which convert them into video and audio signals that can be seen and heard by the viewer.
- Cell phones:Cell phones use radio waves to communicate with cell towers. The cell towers then relay the signals to other cell towers, which allows the cell phones to communicate with each other.
Microwaves
Microwaves are a type of radio wave with a wavelength of between 1 millimeter and 1 meter. They are caused by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields. When an object emits microwaves, it creates a wave of energy that travels through the medium.
Types of Microwaves
- Thermal microwaves:Thermal microwaves are used to heat food. When thermal microwaves are absorbed by food, they cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate, which generates heat.
- Non-thermal microwaves:Non-thermal microwaves are used in a variety of applications, such as radar, satellite communications, and medical imaging.
Examples of How Microwaves Are Used in Everyday Life
- Microwave ovens:Microwave ovens use thermal microwaves to heat food. The microwaves are generated by a magnetron, which is a type of vacuum tube. The microwaves are then directed into the oven cavity, where they are absorbed by the food.
- Radar:Radar uses non-thermal microwaves to detect objects. When a radar system emits a microwave signal, the signal bounces off of objects and returns to the radar receiver. The radar receiver then measures the time it took for the signal to return, which allows it to determine the distance to the object.
- Satellite communications:Satellite communications use non-thermal microwaves to transmit data between satellites and ground stations. The microwaves are transmitted from the ground station to the satellite, which then relays the signal to another ground station.
Top FAQs
What is the speed of sound in air?
The speed of sound in air at room temperature (20°C) is approximately 343 meters per second (1,235 kilometers per hour).
How do radio waves differ from microwaves?
Radio waves have longer wavelengths and lower frequencies than microwaves, and they can travel through solid objects. Microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies, and they are typically used for communication and heating purposes.
What are the practical applications of sound waves?
Sound waves have a wide range of applications, including communication (speech, music), entertainment (music, sound effects), medical imaging (ultrasound), and scientific research (sonar).